SeaBOS aims to minimise antibiotics use by improving overall health management in aquaculture, adopting preventative practices, and implementing a Code of Conduct for responsible antibiotics use. Through data collection, enhanced farm management practices, disease diagnostics, and the development of preventative strategies and resources like vaccines, we strive to promote transparency and accountability. We work collaboratively with diverse stakeholders, including pharmaceutical companies, veterinarians, intergovernmental agencies, and government departments, to develop and improve stewardship and alternatives to antibiotics.
- By October 2021, outline a roadmap to phase out high-risk antibiotics from aquaculture and develop an antibiotic use Code of Conduct.
- Enhance antibiotic survey data and collaborate with expert organizations on alternatives.
- Agree to a roadmap for establishing a “SeaBOS Antibiotics Code of Conduct” by
October 2022. - Extend the Code’s scope to member operations and aquaculture supply
chains. - Cease the use of HPCIA and CIA in aquaculture unless permitted by national
legislation. Commit to annual antibiotic stewardship
surveys to monitor progress.
Our actions & impact (2023)
To reduce antibiotics use, SeaBOS has been developing a Code of Conduct and a roadmap for implementation by our members. In addition, annual reporting of antibiotics usage has been a priority to better inform science and practice on antibiotics in seafood production.
Road Map for Reducing Antibiotic Use
9/9
Shared High-Resolution Data with Scientists
6/9
Science outlook
Scope, scale and urgency of action
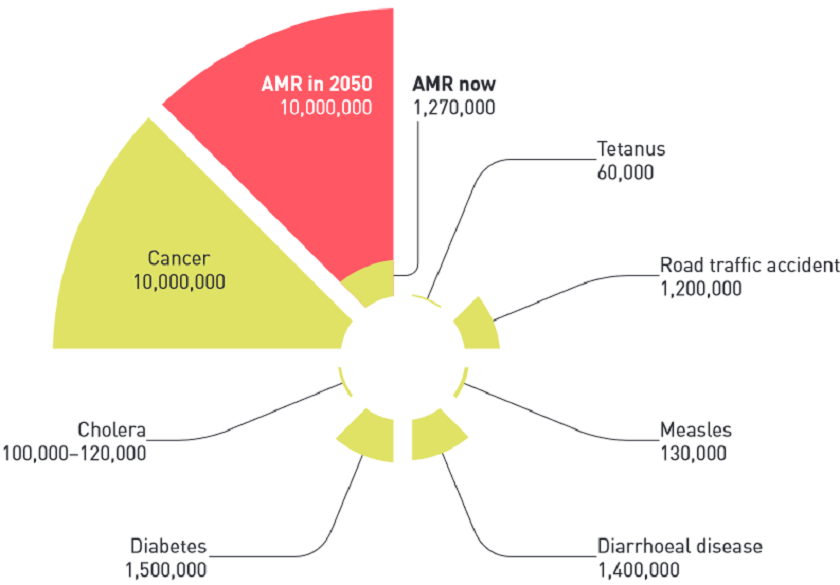
Antibiotic use has contributed to the spread of antimicrobial resistance, an emerging public health crisis estimated by the United Nations to result in up to 10 million deaths annually by 2050. While antibiotics enable greater food production and have importance for animal welfare, considerable scope exists to limit usage by reducing misuse and over-application around the world. Over longer timeframes, the development of vaccines can reduce dependency on antibiotics; in Norway, for instance, vaccines have resulted in the virtual elimination of antibiotics in salmon aquaculture production. Over 600 species are in aquaculture production around the world, but vast gaps exist in knowledge about the quantity and type of antibiotics used in these diverse production systems, hampering action and progress.
Pathways forward
The improper use of antibiotics in aquaculture results in the loss of efficacy of antimicrobials crucial for human healthcare. Focusing on reducing and eventually eliminating the need for Critically Important Antimicrobials for Human Medicine, as identified by the World Health Organization is a crucial priority. A focus on responsible antibiotic use and overall health management is indispensable to ensure the sustainable future of the aquaculture industry. Companies can contribute by providing transparent accessibility of data, engaging in vaccine development, and contributing to eliminating vast knowledge gaps about the frequency and prevalence of antimicrobial resistant genes in production systems around the world.
Case studies

Collaboration for vaccine development
Nissui, Maruha Nichiro and Kyokuyo are working together with Japanese government offices and the pharmaceutical industry in Japan to reduce antibiotics use and develop vaccines that enable a transfer away from the use of highest priority critically important antibiotics (HPCIA).

Establishment of Roadmap and Code of Conduct
The SeaBOS Antibiotics Code of Conduct provides strategies for maintaining fish health and welfare
and reducing use of antibiotics through preventative practices and interventions. Furthermore, the SeaBOS Antibiotic Stewardship Roadmap guides members in the phasing out of HPCIA and CIA in line with World Health Organization (WHO) standards.